What is a Tibia Tarantula Egg
The Tibia Tarantula, a creature of fascinating biology, reproduces through the laying of eggs. The term ‘Tibia Tarantula egg’ refers to the reproductive structure containing the developing embryos of these arachnids. Unlike some other species that give birth to live young, Tibia Tarantulas are oviparous, meaning their offspring develop within eggs outside the mother’s body. These eggs are carefully crafted by the female tarantula, providing a safe environment and essential nutrients for the developing spiderlings. Understanding the nature of these eggs is crucial for anyone interested in the life cycle and care of Tibia Tarantulas, and offers a window into the intricate world of these captivating creatures. The eggs are a critical stage in the life cycle of the Tarantula, ensuring the continuation of the species.
The Origin of Tibia Tarantula Eggs
Tibia Tarantula eggs originate from the reproductive system of the female tarantula. After mating, the female stores sperm and uses it to fertilize her eggs. The eggs are then formed within her abdomen and are coated in a protective layer of silk, produced by the spinnerets located at the rear of the tarantula. This silk forms a protective egg sac, also known as an ootheca, which safeguards the eggs from environmental hazards and predators. The process is an intricate dance of biology and instinct, ensuring the survival of the next generation. This egg sac is a testament to the tarantula’s maternal care, safeguarding the developing eggs until they are ready to hatch. The origin is a critical aspect of the life cycle.
Tibia Tarantula Egg Laying Process
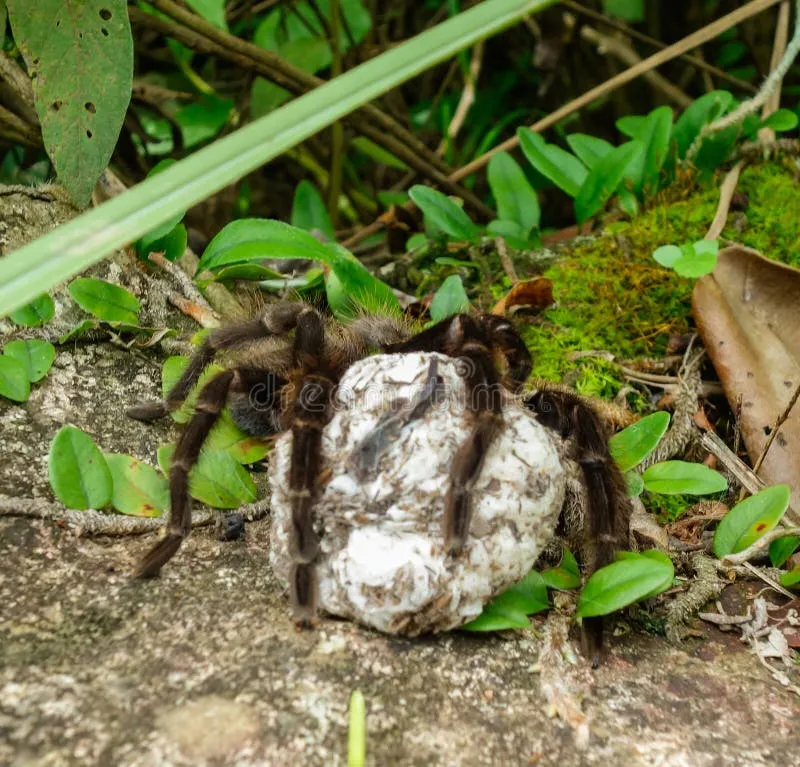

The laying of Tibia Tarantula eggs is a complex and delicate process. Once the eggs are formed and fertilized within the female tarantula’s abdomen, she begins to spin a silk structure. This silk serves as the foundation of the egg sac. The female then deposits the eggs into the silk structure and carefully wraps them within the silk. This wrapping process is crucial as it provides both protection and a stable environment for the eggs to develop. The entire process, from egg formation to the sealing of the egg sac, can take several hours, and the female tarantula remains vigilant in guarding the sac until the spiderlings hatch. The egg laying process is a very important thing to learn.
How Often do Tibia Tarantulas Lay Eggs
The frequency with which Tibia Tarantulas lay eggs can vary depending on several factors, including the species, age, and overall health of the female tarantula. Generally, mature female tarantulas lay eggs once or twice a year. However, this can be influenced by environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, as well as the availability of food. Some species might lay eggs less frequently, while others may have the potential to lay multiple egg sacs within a single mating season. The timing is crucial, often corresponding to optimal conditions for the survival of the spiderlings. This frequency directly impacts population growth within their habitat, making egg-laying a critical aspect of their life cycle.
Factors That Affect Egg Laying
Several factors influence a Tibia Tarantula’s egg-laying behavior. The female’s nutritional status plays a crucial role, as adequate food intake provides the necessary resources for egg production. Environmental conditions, such as appropriate temperature and humidity levels, are also critical for successful egg development. Additionally, the presence of a suitable mate and the successful completion of mating are essential prerequisites for egg laying. Stress and disturbances can negatively impact egg production, potentially leading to fewer eggs or unsuccessful incubation. Understanding these factors is important for anyone caring for or studying Tibia Tarantulas, as they directly affect the reproductive success of these fascinating creatures. Factors that affect egg laying is essential.
Top 7 Facts About Tibia Tarantula Eggs
Fact 1 The Appearance of Tibia Tarantula Eggs
Tibia Tarantula eggs, when carefully observed, present a unique appearance. The eggs are typically spherical or slightly oval in shape, and their color can vary depending on the species and the stage of development. The eggs are often creamy white or yellowish in color. The protective silk egg sac, which encloses the eggs, is usually a tightly woven, pearly white or tan. The appearance of the egg sac is also an indicator of the female tarantula’s health and the eggs’ condition. The overall appearance of the egg sac is very interesting to look at.
Fact 2 The Size and Shape of Tibia Tarantula Eggs
The size and shape of Tibia Tarantula eggs vary depending on the species. Generally, the eggs are quite small, measuring only a few millimeters in diameter. Their shape is typically round or slightly elongated. The egg sac, which contains multiple eggs, can range in size from a small walnut to the size of a golf ball, depending on the number of eggs and the species. These variations in size and shape reflect the evolutionary adaptations and reproductive strategies of different tarantula species, each uniquely suited to their environment. Size and shape is important for the life cycle.
Fact 3 The Incubation Period for Tibia Tarantula Eggs
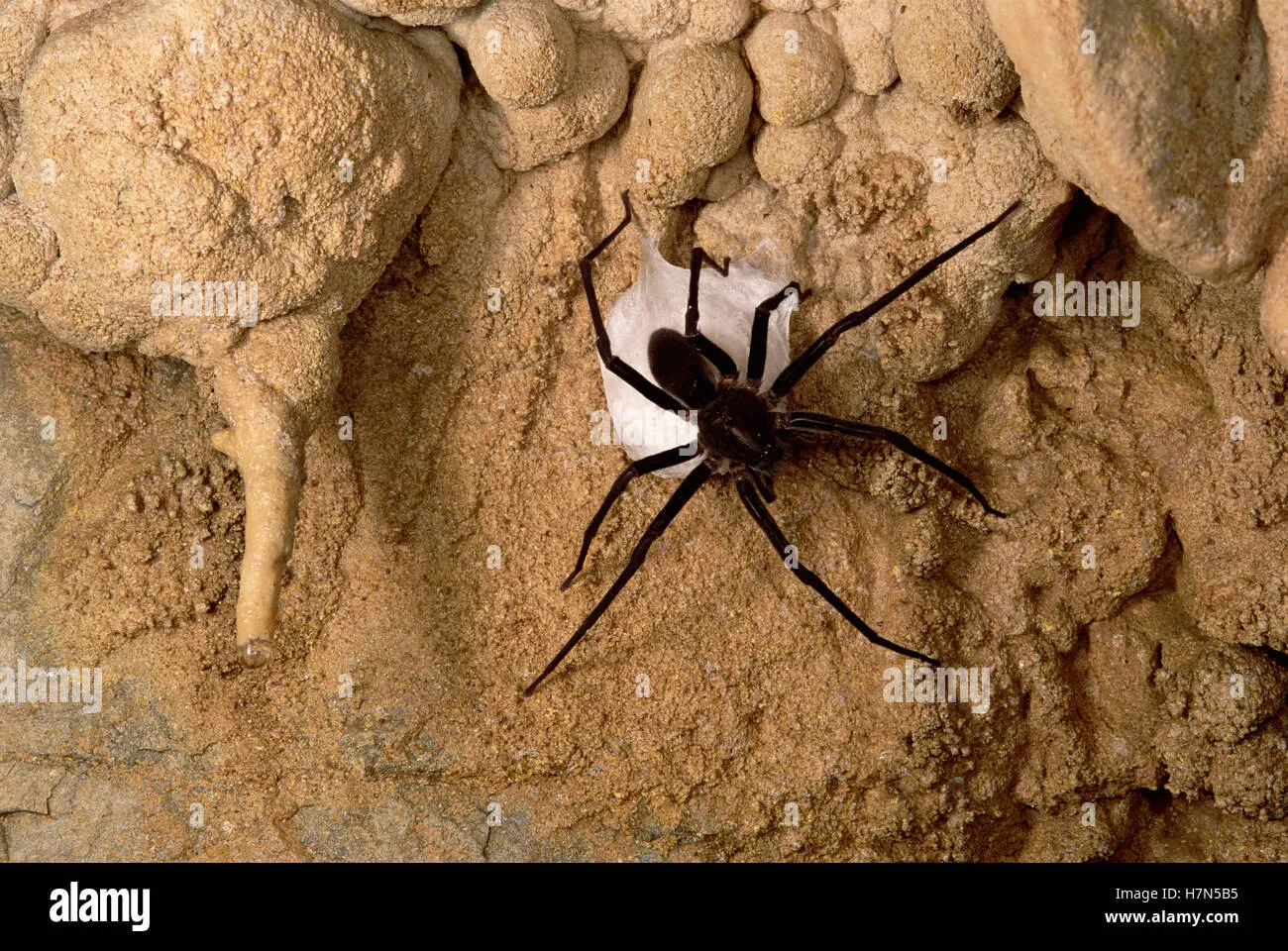

The incubation period, the time it takes for the eggs to hatch, varies among different Tibia Tarantula species and is also influenced by environmental conditions. The average incubation period typically ranges from a few weeks to several months. Warmer temperatures and higher humidity generally accelerate the incubation process, while cooler conditions may extend it. During this period, the eggs develop into spiderlings, undergoing crucial stages of growth within the protective egg sac. Monitoring the incubation period is crucial for breeders, as it provides insights into the health and development of the eggs. The incubation period is important for the survival of the eggs.
Fact 4 What Determines the Gender of Tibia Tarantulas
The sex of a Tibia Tarantula is determined genetically, but it’s not always immediately apparent in the egg stage. The exact mechanisms that determine the sex of tarantulas are complex, and much is still unknown. However, it is believed that genetic factors play a primary role. The environmental factors do not appear to significantly influence sex determination. The determination of gender is very important for breeding.
Fact 5 Predators and Threats to Tibia Tarantula Eggs
Tibia Tarantula eggs face various threats from predators and environmental hazards. Ants, mites, and other small insects can be a significant threat, as they may try to consume the eggs. Fungal infections can also pose a danger, especially in humid environments. Extreme temperatures and fluctuations in humidity can also be detrimental, potentially leading to egg desiccation or improper development. Female tarantulas vigilantly protect their egg sacs, but despite this, some eggs may still fall victim to these threats. Understanding these threats is crucial for successful tarantula breeding and conservation efforts. The survival of the egg is a must to protect the next generation.
Fact 6 The Survival Rate of Tibia Tarantula Eggs
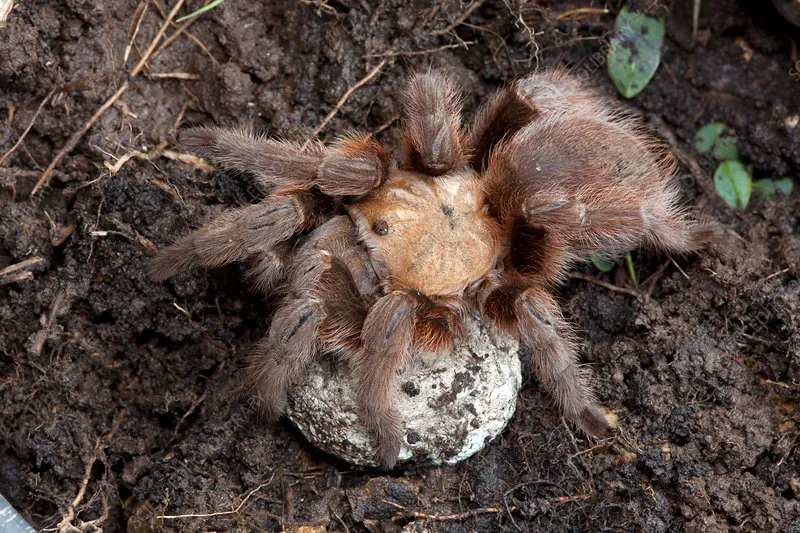

The survival rate of Tibia Tarantula eggs varies depending on several factors, including the species, environmental conditions, and the female tarantula’s care. While some eggs may fail to hatch due to various threats, the overall survival rate is usually relatively high under optimal conditions. Female tarantulas instinctively protect their egg sacs, and provide an environment conducive to development. The survival rate is a testament to the tarantula’s adaptation to its environment. The conditions for survival play a huge part.
Fact 7 Where to Find Tibia Tarantula Eggs
In their natural habitat, Tibia Tarantula eggs are typically found in the burrows or shelters created by the female tarantula. These locations are often concealed to provide protection from predators and environmental hazards. In captive environments, breeders usually provide a suitable environment for the female to lay eggs, mimicking the natural habitat. The eggs are often laid within a silk egg sac, which the female diligently guards until the spiderlings hatch. Finding these eggs is a rewarding experience for enthusiasts and researchers. The ideal place to find these eggs is in their natural habitat.
Caring for Tibia Tarantula Eggs
Ideal Environmental Conditions
Providing the right environmental conditions is crucial for the successful incubation of Tibia Tarantula eggs. Temperature and humidity are the most critical factors. Maintaining a stable temperature within the appropriate range for the species is important, usually between 75-85°F (24-29°C). High humidity levels, typically around 70-80%, should be maintained. Proper ventilation is also important to prevent mold growth. Monitoring these parameters with a thermometer and hygrometer is recommended. Regular checks of the eggs sac are very important. This will help ensure the survival.
Feeding and Hydration of Hatchlings
Once the spiderlings hatch, they require appropriate feeding and hydration. Providing small, live prey items, such as fruit flies or pinhead crickets, is essential for their growth. Ensure the prey is appropriately sized so the spiderlings can easily consume them. Provide a shallow water dish with clean water or use a water source. Monitoring the hatchlings and ensuring they are eating and staying hydrated is a sign of a healthy environment. Regular feeding and hydration schedules are essential for their well-being. The survival of the young ones is essential.
Common Problems and Solutions
Caring for Tibia Tarantula eggs and spiderlings can be challenging, and several common problems may arise. Mold or fungal growth on the egg sac can be a major issue, often caused by excessive humidity or poor ventilation. To combat this, improve ventilation. Another common issue is the failure of the eggs to hatch, which can be caused by various factors, including incorrect environmental conditions, infertile eggs, or predation. Regularly monitor the eggs, maintain optimal conditions, and seek advice from experienced breeders if problems arise. The problems are common, and with a little care the problem is solved.
Conclusion

The Tibia Tarantula egg represents a critical stage in the life cycle of these fascinating creatures. From its origin within the female tarantula to the hatching of spiderlings, the process is a testament to the power of nature. Understanding the facts surrounding Tibia Tarantula eggs, including their appearance, the laying process, incubation, and care, is essential for anyone interested in these arachnids. Proper care and maintenance of the egg sac and hatchlings are vital for the survival and healthy development of the next generation. As you delve deeper into the world of Tibia Tarantulas, the knowledge of their eggs and their life cycle provides a greater appreciation for their complexity and unique biology. Continuing to learn about these creatures is a fulfilling thing to do.
